| Name | Bayer | Mag. | Appendix |
|---|---|---|---|
| Achernar | Alpha Eridani | 0.5 | |
| Acrux | Alpha Crucis | 0.8 | |
| Adhara | Epsilon Canis Majoris | 1.5 | |
| Aldebaran | Alpha Tauri | 0.9 | |
| Algol | Beta Persei | 2.1 (Max) | |
| Altair | Alpha Aquilae | 0.8 | Member of the Summer Triangle, Hikoboshi or Kengyu in Tanabata story |
| Antares | Alpha Scorpii | 0.9 (Max) | |
| Arcturus | Alpha Bootis | -0.0 | Member of the Spring Triangle |
| Betelgeuse | Alpha Orionis | 0.0 (Max) | Member of the Winter Triangle |
| Canopus | Alpha Carinae | -0.7 | |
| Capella | Alpha Aurigae | 0.1 | |
| Castor | Alpha Geminorum | 1.6 | |
| Deneb | Alpha Cygni | 1.2 | Member of the Summer Triangle |
| Denebola | Beta Leonis | 2.1 | Member of the Spring Triangle |
| Fomalhaut | Alpha Piscis Austrini | 1.2 | |
| Hadar | Beta Centauri | 0.6 | |
| Mimosa | Beta Crucis | 1.2 | |
| Mira | Omicron Ceti | 2.0 (Max) | |
| Polaris | Alpha Ursae Minoris | 2.0 | |
| Pollux | Beta Geminorum | 1.1 | |
| Procyon | Alpha Canis Minoris | 0.4 | Member of the Winter Triangle |
| Regulus | Alpha Leonis | 1.4 | |
| Rigel | Beta Orionis | 0.1 | |
| Rigil Kentaurus | Alpha Centauri | -0.3 | |
| Sirius | Alpha Canis Majoris | -1.5 | Member of the Winter Triangle |
| Spica | Alpha Virginis | 1.0 | Member of the Spring Triangle |
| Vega | Alpha Lyrae | 0.0 | Member of the Summer Triangle, Orihime in Tanabata story |
One star can have several names. For example Sirius is Alpha Canis Majoris in Bayer Designations, 9 Canis Majoris in Flamsteed Designations, HIP 32349 in Hipparcos Catalogue and HD 48915 in Henry Draper Catalogue. We used N.D. Kostjuk, HD-DM-GC-HR-HIP-Bayer-Flamsteed Cross Index (2002) to relate those names.
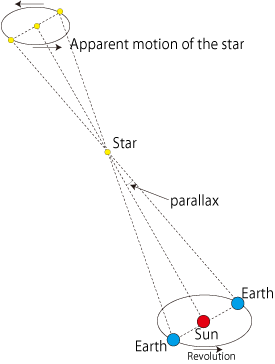
Position of a star changes as the Earth goes around the Sun. We can determine the distance to the stars using the apparent motion named parallax, and the distance between the Earth and the Sun.
Parallax is the proof that the Earth is moving round the Sun. But the parallax of Alpha Centauri, the nearest star, is only 0.7 arcsecond. In fact 16th century astronomer Tycho Brahe believed that Ptolemaic Theory was right since he did not observe any parallax.
Hipparcos satellite (1989) aimed at determining the parallax precisely. Its outcome is the Hipparcos catalogue, and we use its revised version (Hipparcos, the New Reduction, van Leeuwen, 2007). However, even Hipparcos catalogue has its limit, approximately 300 light years. Distance with * means the value is not accurate enough.